This article was written by Mr. Alireza Hassanali, Mr. Navid Hassanali and Mrs. Niloufar Sharafi and was presented by them at the 10th Congress of Infection Control.
Abstract
Goal
Environmental protection is a key issue, and improper disposal of infectious fluids poses irreparable risks to human health and the environment.
Infectious waste is any waste that is generated during a diagnostic process, treatment, or research activities that include biological experiments.
The management of infectious waste is as vital as its disposal, therefore, it is necessary to use products such as disposable suction bags that collect infectious fluids and prevent them from spreading to the surrounding environment.
In this article, we will investigate the issue of Nosocomial Infections and the methods of preventing the spread of this infection, as well as the management of infectious waste using the new method (Disposable Suction Liner Bag) and the old method (Permanent Suction Canisters).
Methods
The study was conducted by the AHP Method model, which is one of the multi-criteria decision-making methods and analyzes the evaluation of parameters quantitatively and qualitatively; also, to use this method and evaluations, Expert Choice software has been used.
Results
It is clear in this study that permanent suction canisters cause hospital infections, increase medical centers’ costs, and increase hospitals’ infectious waste, which costs 10 to 15 times more than other waste due to its infectiousness. Also, the use of disposable suction liner bags not only reduces and controls hospital infections but also reduces the costs of disposal and disposal of infectious waste and treatment of infectious wastes, as well as saving water, electricity, and human resources.
Conclusion
The results of this study allow managers and officials of hospitals and medical centers to know which type of suction canisters to use to improve the level of hospital control and to be familiar with the advantages, disadvantages, risks, and environmental risks caused by suction canisters. to make the best decision in this regard.
Keywords: infectious waste, disposable suction liner bags, permanent suction canisters
Introduction
Preservation of the environment is a key issue, and incorrect methods of hospital infectious waste management pose irreparable risks to human health and the environment and cause disease.
One of these diseases is hospital infections; Today, in most hospitals and medical centers, we see patients who get hospital infections about 48 to 72 hours after being hospitalized, according to the CDC report, 1 patient out of every 31 hospitalized patients gets hospital infections every day, and the cost associated with Nosocomial Infections in the United States is estimated to be up to $25,000 per infection.
Therefore, it is necessary to use products such as disposable suction bags that turn infectious hospital effluents into waste and prevent the spread of infectious effluents into the environment.
In this presentation, we will examine the management of infectious wastes using the new method (disposable suction liner bags) and the old method (permanent suction canisters).
Hospitals and medical centers always play a vital role in the welfare and health of humanity; One of the problems that medical centers are involved in is the management of waste and hospital effluents, which cause various infections, pathogens, and environmental hazards.
Improper methods of hospital effluent and waste management around the world can have a direct and indirect impact on human health and the environment and cause disease.
One of these diseases is hospital infection; Hospital infection (healthcare-associated infection) is an infection that occurs during the treatment process and is not present when the patient is admitted to the hospital. This infection may occur in different departments of the hospital, care centers, and outpatient departments of health centers. and it is even possible to appear after the patient is discharged from the treatment center.
In addition to patients, hospital infections affect the medical staff and their companions and bring significant costs to hospitals and medical centers.
As a result of the correct management and collection of infectious fluids, the risk of the spread of hospital infections will decrease, and as a result, the death rate from hospital infections will decrease; In the past few decades, compliance with hospital infection control protocols has significantly reduced the number of deaths caused by hospital infections.
In this article, we are going to discuss waste and infectious waste and their collection methods, and the environmental and health effects of suction canisters, as well as compare the effects of permanent canisters and disposable suction liner bags, and finally, the experience of advanced countries in we analyze the use of disposable suction liner bags.
The Necessity Of The Issue
Among the harmful effects of hospital infections are:
- Increased risk of cancer
- Gene mutation
- Growth and proliferation of pathogenic and infectious bacteria
- The outbreak of various diseases
Also, among the effects of the uncontrolled discharge of infectious liquids into the sewage, we can mention damage to the facilities of the collection network and sewage treatment plant, disruption of the sewage treatment process, environmental pollution, and threat to the health of society.
The Necessity Of Converting Infectious Effluent Into Waste
The infectious wastewater treatment process is more complicated than infectious waste.
Vast amounts of water must treat in hospital wastewater to bring the parameters in hospital wastewater to the standard.
Reducing the production of infectious waste (personal protective equipment)
Methodology
The study was conducted by the AHP Method model, which is one of the powerful decision-making techniques and analyzes the evaluation of parameters quantitatively and qualitatively; also, to use this method and evaluations, Expert Choice software has been used.
|
No |
Description |
Amounts |
| 1 | Wasting water |
15 Liters of water per canister |
|
2 |
Wasting disinfectants |
500 cc |
|
3 |
The risk of permanent canisters breaking during washing |
Risky |
| 4 | Contamination of hospital wastewater |
Risky |
|
5 |
Leakage during suction operation | Risky |
| 6 | Excessive electricity consumption |
Risky |
|
7 |
Increasing hospital infectious waste |
Risky |
Quantity Risks Due To The Use Of Permanent Suction Canisters
|
No |
Description |
|
1 |
The risk of spreading the contents of the canisters during washing to the treatment staff |
|
2 |
The risk of not washing the permanent canisters completely and correctly due to the lack of time between 2 operations |
|
3 |
The risk of wasting the time of the treatment staff by washing |
|
4 |
The risk of slipping the treatment staff during washing |
|
5 |
The risk of contracting hepatitis C and HIV during washing |
|
6 |
The risk of contamination through the permanent canisters of the suction device |
|
7 |
The risk of developing nosocomial infection and increasing the duration of hospitalization |
|
8 |
Risk of transmission of infection and contamination of hospital wastewater during discharge |
| 9 |
Increased risk of human errors due to manual assembly |
Qualitative risks caused by the use of permanent suction canisters (research method: use of AHP METHOD statistical method in field research by the researcher)
Findings
To carry out this research, we evaluated and reviewed all the things involved in this issue, including the washing method, costs, waste disposal, wastewater treatment, etc., so that we can come to the conclusion which They are more economical than permanent suction canisters and disposable suction bags and are better for use in the environment and cause less damage to the environment. The above comparisons can be seen in the following tables.
Comparison of the washing process
|
No |
Description |
Amounts |
| 1 | Water |
10 liters |
|
2 |
Disinfectants |
Corsolux Plus 2% (in a ratio of 1 to 10) |
|
3 |
Workers |
1 Person |
|
4 |
Time |
30 minutes |
| 5 | Disposable Latex Gloves |
1 |
|
6 |
Medical Disposable Apron |
1 |
|
7 |
Medical Safety Glasses |
The patient is in the high-risk group |
|
8 |
Filtered Mask |
The patient has pulmonary tuberculosis |
| 9 | At the risk of exposing the treatment staff |
Hepatitis C and HIV |
Comparison table of washing permanent suction canisters and disposable suction liner bags
|
No |
Description | Permanent suction canisters |
Disposable suction liner bag |
|
1 |
Annual water consumption in Iran | 130,000,000 liters |
0 liter |
|
2 |
Annual consumption of disinfectants | 175,000,000,000 billion Tomans |
0 Rial |
| 3 | Workers | 30 minutes per canister |
0 minute |
|
4 |
Personal protective equipment | 20,000 Tomans per canister |
0 Rial |
|
5 |
The cost of a disposable suction liner bag per year | 0 |
400 billion Rial |
Comparison table of costs caused by permanent suction canisters and disposable suction bags
Advantages of using disposable suction liner bags
- Removal of a significant part of infectious hospital effluents
- Reducing and controlling the risk of Nosocomial Infections
- Elimination of the process of washing and disinfection of permanent suction canisters
- Reducing per capita wastewater production in hospitals
- Eliminate the risk of spreading dangerous microorganisms to the environment
- Reducing costs related to the destruction of infectious waste
- Time management of the treatment staff
Eliminating the risk of the treatment staff contracting hepatitis C and HIV during washing.
The World Trend Is Using Disposable Suction Liner Bags
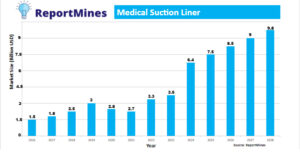
Disposable Suction liner Bags Market Research Report
The global disposable suction liner bags market size is projected to reach several million people by 2028 compared to 2021 at an unexpected CAGR from 2022 to 2028.
The chart below shows developed and developing countries using disposable suction liner bags
|
Row |
Continent |
Countries |
|
1 |
North America |
United States, Canada |
|
2 |
Europe |
Germany, France, England, Italy, Russia |
|
3 |
Asia and Oceania |
China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, China, Taiwan, Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia |
|
4 |
Latin America | Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Colombia |
| 5 | Middle East and Africa |
Turkey, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates |
Conclusion
What is clear in this research and investigation is that the use of permanent suction canisters causes an increase in Nosocomial Infections in hospitals, the creation of hospital-acquired infectious diseases, and an increase in the costs of medical centers.
But the Disposable Suction Liner Bag not only reduces and controls the disease, preserves the health of the treatment staff, and also saves water, electricity, and human resources.
References:
- https://www.cdc.gov/hai/data/index.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/hai/pdfs/hai/scott_costpaper.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559312/
- Boev C, Kiss E. Hospital-Acquired Infections: Current Trends and Prevention. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2017 Mar;29(1):51-65. [PubMed]
- National Research Council (US) Committee on Hazardous Biological Substances in the Laboratory. Biosafety In The Laboratory: Prudent Practices for the Handling and Disposal of Infectious Materials. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1989. 4, Safe Disposal of Infectious Laboratory Waste. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK218626/
- Kaye, Keith, et. al. (2010). Suction regulators: a potential vector for hospital-acquired pathogens. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, 31(7), 772-774.
- Maragakis, Lisa, et. al.(2004). An outbreak of multidrug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii associated with pulsatile lavage wound treatment. JAMA, 292(24), 3006-3011.
- “Use of Filters on Medical Gas System Outlets and Vacuum System Inlets” User Experience Network™, ECRI [Health Devices Dec 1994;23(12):494-5].
- Guidelines for Design and Construction of Healthcare Facilities: Facility Guidelines Institute; 2010 Edition. § 2.1-8.4.4.2 Vacuum systems
- Neary, Michael, et. al “The Clinical Importance of Unrestricted Flow in Hospital Suction Systems” Clinical white paper published August 2008 by Boehringer Laboratories, LLC
- Hill, John, et. al ”The Efficacy of Backflushing Suction Regulators as a Method of Internal Disinfection” Presented at the 55th Annual International Respiratory Conference (AARC 2009).
- Kaye, Keith, et. al ”An Evidence-Based Approach to Determining Hospital Suction Canister Change Protocols” Presented at the 37th Annual Meeting of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC 2010).





































3 Responses
perfect
Awsome
Amazing