Introduction
Securing and maintaining a safe airway is one of the fundamental principles of patient care in intensive care units (ICUs), operating rooms, and emergency settings. Endotracheal intubation, as a critical intervention, plays a key role in providing respiratory support for critically ill, unconscious, or respiratory-compromised patients. Despite its importance, multiple challenges exist in the proper fixation and maintenance of endotracheal tubes, which, if inadequately managed, can lead to significant clinical complications.
Unintended movement or displacement of the endotracheal tube, oral and lip mucosal injuries, pressure ulcers, difficulty in performing oral care, and an increased risk of hospital-acquired infections are common issues in intubated patients. These challenges are particularly pronounced in patients with reduced consciousness, agitation, delirium, or limited cooperation, placing additional strain on healthcare staff. Therefore, the use of specialized devices for secure and stable tube fixation has become a clinical necessity.
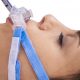
Endotracheal tube fixators are specialized devices designed to maintain correct tube positioning, minimize tissue damage, and facilitate nursing care. By providing mechanical stability and improved access to the oral cavity, fixators can play a significant role in enhancing patient safety, improving quality of care, and supporting infection control. With increasing emphasis on patient-centered care and the prevention of avoidable complications, endotracheal tube fixators have emerged as an essential component of modern respiratory care.
Challenges in Patients with Low Cooperation for Tube Fixation
One of the primary challenges in caring for intubated patients is achieving secure and stable fixation in individuals with low cooperation. This group includes patients with decreased consciousness, agitation, delirium, brain injuries, sedative medications, or those dependent on prolonged mechanical ventilation. In these cases, maintaining proper tube position without specialized devices is difficult and risky.
In low-cooperation patients, sudden head or jaw movements, involuntary attempts to remove the tube, and resistance to medical interventions significantly increase the risk of tube displacement, kinking, or accidental extubation. Such events can have serious consequences, including sudden ventilation failure, hypoxemia, the need for re-intubation, and increased risk of airway injury. Each re-intubation not only causes stress for the patient but also increases the workload and risk of clinical errors for healthcare staff.
Traditional tube fixation methods, such as standard adhesive tapes or non-specialized straps, are often ineffective in low-cooperation patients. They do not withstand moisture, oral secretions, or perspiration and can easily loosen. Additionally, asymmetric tension from tapes can exert excessive localized pressure on the lips and oral mucosa, predisposing patients to pressure ulcers, skin irritation, and soft tissue injury.
Patients with low cooperation often require repeated interventions to adjust tube position. These repeated manipulations increase patient discomfort and stress and elevate the risk of microbial contamination and infection transmission. Moreover, limited access to the oral cavity due to improper fixation complicates oral hygiene and suctioning procedures, increasing the likelihood of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) and other infections.
In this context, the use of standardized endotracheal tube fixators offers an effective solution. Fixators provide uniform, stable fixation, reduce the need for repeated handling, and ensure proper oral access, maintaining airway safety even in low-cooperation patients. This not only prevents clinical complications but also reduces staff workload and improves overall quality of patient care.
Prevention of Oral Ulcers and Tissue Injury
A common yet preventable complication in intubated patients is the development of oral ulcers and soft tissue injuries around the lips, cheeks, and oral mucosa. Continuous pressure from the tube, improper fixation, and prolonged use of non-standard securing methods can impair local blood flow, cause tissue necrosis, and lead to pressure ulcers. These complications not only cause patient discomfort and pain but also increase the risk of secondary infections and prolonged hospitalization.
Traditional fixation methods, such as non-ergonomic tapes or straps, often create uneven, localized pressure on sensitive oral areas. In immobile or low-cooperation patients, this sustained pressure can result in redness, inflammation, superficial ulcers, and, in severe cases, deep mucosal injuries. Direct contact of adhesives with moist and sensitive oral skin can also cause irritation, contact dermatitis, and superficial skin layer separation.
Intubated patients are further predisposed to oral dryness and tissue vulnerability due to reduced saliva, mouth breathing, and certain medications. In these conditions, additional pressure or friction from improper tube fixation significantly increases the risk of tissue damage, which can delay recovery and negatively impact the patient’s care experience.
Standardized endotracheal tube fixators play a crucial role in preventing these issues. Ergonomic designs and skin-friendly materials allow uniform pressure distribution, preventing concentrated stress points. Adjustable tube positioning further ensures that pressure is not localized, reducing tissue injury risk.
By providing stable fixation, fixators also reduce the need for repeated tube handling, thereby minimizing friction and continuous irritation of the oral mucosa. Overall, the use of endotracheal tube fixators effectively prevents oral ulcers and enhances the quality of care for intubated patients.
Enhancing Patient Satisfaction and Care Experience
Patient satisfaction is a key indicator of healthcare quality and, alongside clinical outcomes, is essential for evaluating healthcare performance. Intubated patients, particularly in ICUs, often face communication barriers, discomfort, anxiety, and loss of control, creating a stressful treatment experience. Minimizing distressing factors and maximizing comfort is critical to improving the patient’s care experience.
Improper tube fixation can cause continuous oral and lip irritation, pressure, pain, and agitation, even in patients with reduced consciousness. These discomforts often trigger involuntary movements, attempts to remove the tube, and a cycle of agitation and repeated interventions. Using a standardized fixator reduces these tensions by providing stability and minimizing localized irritation, creating a calmer physical and psychological environment for the patient.
Reducing the need for repeated tube handling is also crucial for enhancing patient comfort. Every adjustment or repositioning can cause pain, discomfort, or increased anxiety. Fixators maintain stable tube positioning, decrease the frequency of interventions, and establish a predictable, low-stress care routine, which is particularly beneficial for long-term ICU patients.
Patient satisfaction extends beyond physical comfort to overall care quality. Proper tube fixation facilitates better oral care, effective suctioning, and prevention of complications. While these actions may not be directly perceived by the patient, they indirectly reduce complications, shorten hospital stays, and improve clinical outcomes, contributing to a more positive treatment experience.
In summary, endotracheal tube fixators balance safety, comfort, and care quality, playing a pivotal role in enhancing patient satisfaction. Their use reflects a patient-centered approach to respiratory care, emphasizing not only survival but also the human experience during treatment.
Facilitating Oral Hygiene for Nurses and Healthcare Staff
Oral hygiene is a critical component of care for intubated patients, particularly for preventing respiratory infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). In clinical practice, performing effective oral care in intubated patients is often challenging, primarily due to limited access caused by improper tube fixation.
Traditional fixation methods often cover large portions of the mouth, obstructing access for cleaning, suctioning, and inspection of oral mucosa. This not only increases the time required for oral care but also raises the risk of incomplete or irregular hygiene, promoting secretion accumulation, microbial growth, and infections.
Endotracheal tube fixators, with ergonomic and standardized design, provide controlled and unobstructed access to the oral cavity. Nurses can perform essential oral care without destabilizing the tube. Improved access allows for faster, safer, and more effective procedures, including brushing, rinsing, mucosal moisturizing, and suctioning.
Additionally, reducing repeated tube manipulations during oral care decreases patient stress and enhances clinical safety. Nurses can provide routine care confidently without fearing accidental tube displacement, improving both care quality and workflow efficiency.
Overall, tube fixators facilitate oral hygiene, allowing healthcare staff to deliver safer, more effective, and standardized care while reducing time and effort.
Enhancing Cleanliness and Infection Control
Infection control is a critical priority in hospitalized patients, especially those in ICUs requiring mechanical ventilation. The oral cavity and upper airway are major sources of microbial contamination, which, without proper hygiene, can lead to VAP and other respiratory infections. Improper tube fixation and restricted oral access promote secretion accumulation and microbial growth, complicating infection control.
Ergonomic tube fixators ensure stable tube positioning without obstructing oral access, aiding in oral cleanliness. They allow healthcare staff to effectively suction secretions, clean the mouth, and perform routine hygiene. Reduced tube manipulations lower the risk of microbial contamination and cross-infection.
Standardized fixators also improve secretion control and prevent accidental contact between contaminated surfaces and hands or tools. This reduces cross-infection risk while protecting healthcare staff. Correct and stable tube fixation is therefore an integral component of infection prevention strategies in ICUs and operating rooms.
Using endotracheal tube fixators helps maintain oral cleanliness, reduce microbial load, and prevent hospital-acquired infections, while enabling safe and effective care delivery. This makes fixators essential tools in modern respiratory care.
Conclusion and Abadis’ Approach to Patient-Centered Care
Proper endotracheal tube fixation is a crucial aspect of caring for intubated patients, directly impacting patient safety, care quality, and staff satisfaction. Challenges such as low cooperation, risk of oral ulcers, difficulty in oral hygiene, and infection risk are central concerns. Standardized, ergonomic tube fixators address these challenges, providing significant benefits for both patients and healthcare staff.
Key benefits include:
-
Enhanced tube stability and airway safety, even in low-cooperation patients
-
Prevention of oral ulcers and tissue injuries
-
Increased patient comfort, satisfaction, and care experience
-
Facilitated oral care for nurses and staff
-
Improved cleanliness and infection control
These advantages not only improve patient safety and well-being but also reduce staff workload and enable accurate, safe, and standardized care delivery.
Abadis consistently focuses on developing innovative, standardized, and practical medical devices to create solutions that satisfy both patients and healthcare providers. Their patient-centered approach emphasizes clinical needs, reduction of complications, simplified care processes, and overall care quality improvement. The endotracheal tube fixator exemplifies this approach, demonstrating Abadis’ commitment to enhancing patient experience, improving safety, and supporting healthcare staff.
Ultimately, specialized devices like endotracheal tube fixators are not only a part of standard clinical care but also represent a significant step toward implementing modern, safe, and humane respiratory care practices, combining technology with patient-centered solutions.
References
-
Gupta, S., & Kapoor, A. (2018). Endotracheal Tube Securing Devices: A Review of Techniques and Complications. Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology, 34(3), 321–328.
-
Gravenstein, N., & Henthorn, T. K. (2017). Airway Management in the Intensive Care Unit. Critical Care Clinics, 33(2), 237–255.
-
Kollef, M. H., et al. (2005). Prevention of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in the Intensive Care Unit. Critical Care Medicine, 33(3), 525–534.
-
American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACN). (2016). Practice Alert: Oral Care for Patients Receiving Mechanical Ventilation.
-
Bailey, B., & McGrath, B. (2014). Patient Comfort and Safety with Endotracheal Tube Securing Devices. British Journal of Nursing, 23(12), 672–679.
-
Hospitals for a Healthy Environment (H2E). (2019). Reducing ICU Infections Through Effective Airway Management.
-
Cook, T. M., et al. (2011). Major Complications of Airway Management in the Intensive Care Unit: Epidemiology and Prevention. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 106(6), 746–754.
-
Fischer, R., & Wenzel, V. (2019). Endotracheal Tube Fixation in Critically Ill Patients: Clinical Considerations and Device Evaluation. Intensive Care Medicine, 45(11), 1525–1535.