Evaluating the Role of Abadis Disposable Suction Bags in Reducing Water Consumption and Improving Healthcare Efficiency
Abstract
The use of disposable suction bags in healthcare facilities has emerged as an effective and practical solution for optimizing hospital wastewater management, reducing the risk of healthcare-associated infections, and decreasing water consumption. The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of proper hospital waste and wastewater management and recommends the adoption of innovative methods to minimize environmental and health hazards.
By utilizing advanced technologies in the production of medical equipment, Abadis Med Company has successfully reduced hospitals’ reliance on traditional and costly suction systems, taking a major step toward environmental preservation. This article examines the impact of Abadis disposable suction bags on water conservation in healthcare centers and evaluates their hygienic and economic benefits.
Given the growing concerns about water scarcity and the need for efficient resource management in healthcare, the use of disposable suction bags can play a crucial role in reducing water consumption. Data collected from several hospitals in Tehran before and after implementing Abadis disposable suction systems show a significant reduction in water use, as well as a decrease in the costs associated with washing and disinfecting reusable suction containers.
The study also explores the collaboration between hospital medical staff and Abadis in improving product quality through the PMCF (Post-Market Clinical Follow-up) process.
Keywords: Disposable suction bag, Abadis, healthcare facilities, water conservation, hygiene, cost reduction
Introduction
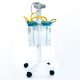
In healthcare environments, infection control and resource optimization—especially concerning water and energy—are among the most critical challenges. One key piece of equipment that has a significant impact in this area is the disposable suction bag. Replacing conventional reusable suction containers, this innovation not only reduces the risk of hospital-acquired infections but also contributes to substantial water savings and enhances staff safety.
Abadis Med Company, as the first and largest manufacturer of disposable suction bags in Iran, has developed products based on advanced technologies and international standards. These disposable systems improve hospital hygiene and safety while providing better cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. Research has shown that using disposable suction bags significantly reduces healthcare workers’ direct contact with infectious fluids and eliminates the need for washing and sterilizing containers — resulting in major savings in both water and hospital operating costs.
Through extensive cooperation with healthcare centers across the country, Abadis has implemented a PMCF (Post-Market Clinical Follow-up) process to collect clinical data and continuous feedback from hospitals. This ongoing quality improvement cycle ensures that product performance aligns with real-world hospital needs.
This article focuses on the impact of Abadis disposable suction bags on water conservation, operational efficiency, and safety in healthcare settings.
Materials and Methods
In this study, data on hospital water consumption in Iran were collected and analyzed before and after the adoption of Abadis disposable suction systems. The research included documentation review, interviews with medical staff, and analysis of cost-related data to assess operational improvements. Furthermore, the collaboration between hospital teams and Abadis through the PMCF process was evaluated for its contribution to ongoing product enhancement.
Water Conservation Achievements
One of the most notable benefits of using disposable suction bags is the significant reduction in water consumption across healthcare facilities. Traditional systems required frequent washing of glass jars or reusable suction canisters—consuming thousands of liters of water per hospital every month.
By adopting Abadis disposable suction technology, hospitals have eliminated the need for repeated washing and disinfection, leading to measurable water savings and reduced use of chemical disinfectants.

Implementation in Hospitals
Abadis disposable suction bags are now in use in over 500 hospitals across Iran, including educational, private, and public healthcare facilities. These institutions have adopted the technology to enhance patient safety, reduce operating costs, and optimize resource utilization.
The use of Abadis suction systems has not only improved hygiene standards but also reduced the workload of hospital staff by eliminating time-consuming sterilization processes. As a result, hospitals benefit from increased efficiency, better infection control, and more sustainable environmental practices.
Results and Case Study of Hospitals
1. Milad Hospital (Tehran)
Milad Specialty and Subspecialty Hospital, located on Hemmat Highway next to Milad Tower in Tehran, is one of the largest and most advanced medical centers in Iran. With a capacity of 1,000 active beds, this hospital provides a wide range of specialized and subspecialized medical services. It includes several dedicated departments such as a 16-bed Surgical ICU, a 7-bed Neurosurgical ICU, a 23-bed CCU, and 9 operating rooms.
Studies indicate that after implementing Abadis disposable suction bags, the hospital experienced a significant reduction in water consumption — with an estimated annual water saving of over 17,325 liters. Additionally, approximately 1,732 liters of blood-contaminated and infectious fluids were safely collected and disposed of.
This level of saving is based on the fact that currently only one operating room department at Milad Hospital uses Abadis products. If the hospital equips all its operating rooms, CCU, and ICU units with these systems, the amount of water savings could increase by at least 14 times.

2. Tandis Hospital (Tehran)
Tandis Super Specialty Hospital was inaugurated in July 2018 in northern Tehran, located on Nelson Mandela Boulevard (Jordan), Tandis Street, No. 2, with a capacity of 63 active beds and various specialized and subspecialized departments.
By using Abadis disposable suction bags, the hospital has successfully achieved an annual water saving of 101,475 liters and safely **collected 10,147 liters of infectious fluids.

3. Nikan Hospital (Tehran)
Nikan Hospital is one of the country’s advanced and specialized medical centers, with a capacity of 102 active beds. By utilizing Abadis disposable suction bags, the hospital has succeeded in saving 264,000 liters of water annually. Additionally, this medical center has safely collected 26,400 liters of infectious fluids per year, significantly improving hygiene standards and operational efficiency.

4. Akhtar Hospital (Tehran)
Akhtar Hospital, located in Tehran’s Shariati Street, Pol-e Romi, Sharifimanesh Street, Azar Alley, is one of the country’s leading orthopedic specialty centers. With a capacity of 120 active beds, it includes specialized departments such as General ICU, CCU, Open Heart ICU, and NICU.
By implementing Abadis disposable suction bags, Akhtar Hospital has successfully saved 74,250 liters of water within one year. Additionally, the hospital has collected 7,425 liters of infectious fluids during the same period, significantly contributing to improved infection control and environmental health.

5. Yas Hospital Complex (Tehran)
Yas Hospital Complex, located in Tehran’s Valiasr Square, Karimkhan Zand Street, North Ostad Nejatollahi (Villa) Street, near Sarv Street, is one of the country’s major specialized and subspecialized medical centers with a capacity of 267 active beds.
By utilizing Abadis disposable suction bags, the hospital has achieved an annual water saving of 138,600 liters and has collected approximately 13,860 liters of infectious waste.
This achievement highlights the hospital’s commitment to sustainable healthcare practices, infection control, and efficient resource management through the adoption of advanced medical technologies.

6. Pars Hospital (Tehran)
Pars Hospital, one of Tehran’s leading and most advanced medical centers, is located at No. 67, Keshavarz Boulevard, Valiasr Square. With a capacity of 191 inpatient beds, the hospital provides specialized services in general surgery, cardiology, neurosurgery, and emergency care.
By implementing Abadis disposable suction bags, Pars Hospital has achieved an annual water saving of 159,637 liters, significantly reducing operational costs and contributing to the preservation of water resources.
Additionally, the hospital has successfully collected 15,963 liters of infectious waste annually using Abadis suction systems — a clear indicator of improved infection control and commitment to sustainable healthcare management.

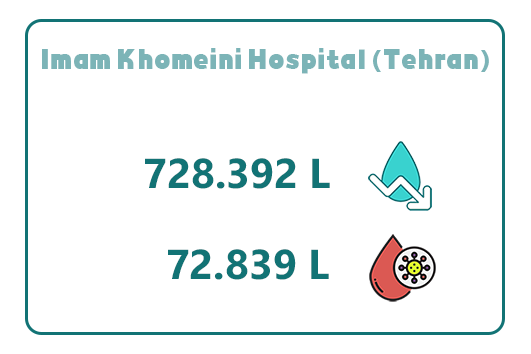
7. Imam Khomeini Hospital (Tehran)
Imam Khomeini Hospital, located at the western end of Keshavarz Boulevard, with a capacity of 1,150 inpatient beds, is recognized as one of the largest and most advanced medical centers in Iran, providing a wide range of specialized and subspecialized healthcare services.
Through the implementation of Abadis disposable suction bags, the hospital has successfully reduced its annual water consumption by 728,392 liters. In addition to this, it has managed to collect 72,839 liters of infectious waste within a year.
This improvement has led to a significant reduction in equipment maintenance and sterilization costs, while also enhancing hygiene standards and operational efficiency across various hospital departments.
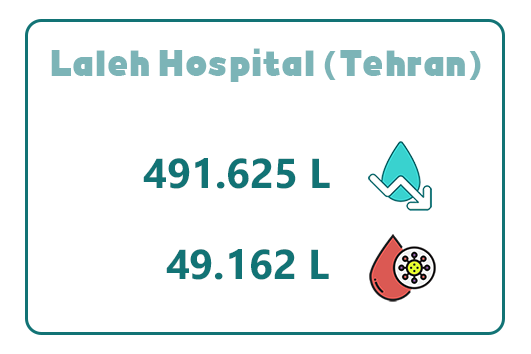
8. Laleh Hospital (Tehran)
Laleh Specialized and Subspecialized Hospital in Tehran, with a total area of over 33,000 square meters, operates 240 approved beds, with the capacity to expand to 420 beds.
By utilizing Abadis disposable suction bags, the hospital has achieved an annual water savings of 491,625 liters. This significant reduction in water consumption has not only improved sanitary processes but also lowered the hospital’s operational costs.
In addition to water conservation, Laleh Hospital has successfully collected 49,162 liters of infectious waste over the course of one year, contributing to enhanced infection control and environmental health.
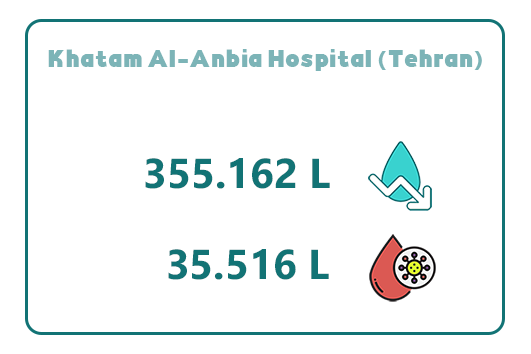
9. Khatam Al-Anbia Hospital (Tehran)
Khatam Al-Anbia Hospital, located on Valiasr Street, north of Mirdamad Boulevard, Rashid Yasemi Street, with a capacity of 480 inpatient beds, is one of Tehran’s advanced medical centers.
By implementing Abadis disposable suction bags, the hospital has achieved an annual water savings of 355,162 liters. This reduction has significantly decreased water consumption across various departments, including emergency and surgical units.
Additionally, within one year, Khatam Al-Anbia Hospital has successfully collected 35,516 liters of infectious waste using disposable suction bags, leading to enhanced hygiene, infection control, and reduced operational costs.
10. Atieh Hospital (Tehran)
Atieh Hospital, with a capacity of 350 beds, provides specialized medical services in fields such as surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, and internal medicine. By using Abadis disposable suction bags, the hospital has achieved an annual water saving of 261,112 liters.
This change has not only contributed to significant water conservation but has also improved the overall quality of healthcare and hygiene practices within the hospital.
Over the course of a year, Atieh Hospital has also managed to collect 26,111 liters of blood-contaminated and infectious waste using the disposable suction bag system.

11. Erfan Hospital (Tehran)
Erfan Specialized and Subspecialized Hospital, located in the Saadat Abad district of Tehran, is one of the country’s leading private medical centers. Built on a 4,480-square-meter land area with a 20,000-square-meter building over nine floors, the hospital has 200 active beds, including private rooms, double rooms, VIP rooms, and 70 intensive care beds.
By using Abadis disposable suction bags, Erfan Hospital has achieved an annual water saving of 432,025 liters and has successfully collected 43,205 liters of infectious waste within a year.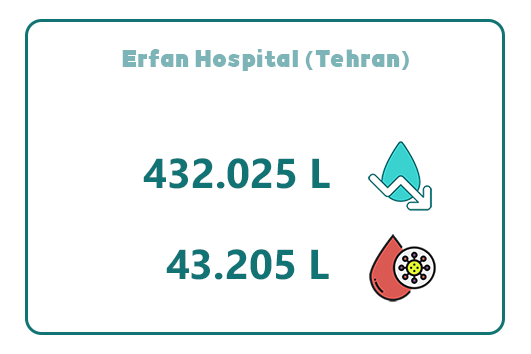
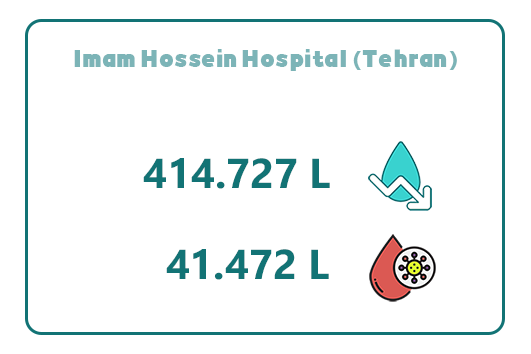
12. Imam Hossein Hospital (Tehran)
Imam Hossein Hospital in Tehran, located on Shahid Madani Street, is the largest educational, research, and medical center affiliated with Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences. With 622 approved beds, this hospital was formed through the merger of three medical centers: Jorjani, Hashtom-e Shahrivar, and Shahid Sahami.
By using Abadis disposable suction bags, Imam Hossein Hospital has achieved an annual water saving of 414,727 liters and has collected 41,472 liters of infectious waste within a year. This initiative has not only reduced the hospital’s operational costs but also played a significant role in environmental protection and improving hospital hygiene.
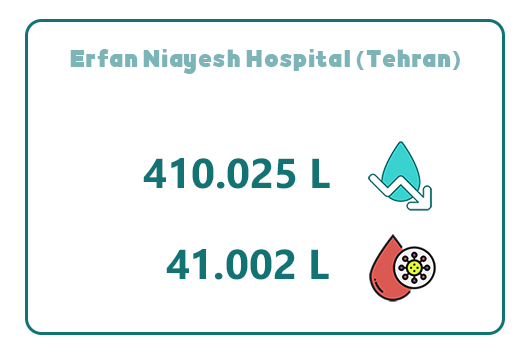
13. Erfan Niayesh Hospital (Tehran)
Erfan Niayesh Hospital, located on West Niayesh Highway, after Kabiri Taameh Boulevard, Imam Hossein Street, at the intersection of Bahar Street, No. 17, is one of the largest private hospitals in Iran, covering a wide range of medical specialties.
Built on a 5,000-square-meter plot with a total floor area of over 31,000 square meters across 11 floors, the hospital includes 250 inpatient beds, featuring over 60 intensive care beds and 23 fully equipped operating rooms.
Through the use of Abadis disposable suction bags and several years of collaboration with Abadis Med Company, Erfan Niayesh Hospital has successfully reduced its annual water consumption by 410,025 liters and collected 41,002 liters of infectious waste each year.
14. Masih Daneshvari Hospital (Tehran)
Masih Daneshvari Hospital, located in northern Tehran, is one of Iran’s leading specialized and subspecialized medical centers and is recognized as the national hub for pulmonary diseases and lung transplantation. The hospital operates with 300 active beds, including ICU, CCU, emergency, surgical, and internal medicine units, providing extensive care for patients with respiratory and infectious diseases.
Through the implementation of Abadis disposable suction bags and its long-term collaboration with Abadis Med Company, Masih Daneshvari Hospital has successfully reduced its annual water consumption by 339,157 liters and collected 33,915 liters of infectious waste per year. The use of this technology has played a significant role in improving hygiene standards, reducing operational costs, and enhancing infection control within the hospital.